Facet Joint Syndrome is a common yet often overlooked cause of chronic neck and back pain. The facet joints are small stabilizing joints located between and behind adjacent vertebrae in the spine. When these joints become irritated or damaged, they can lead to persistent pain and limited mobility. At Kansas Pain Management, we specialize in diagnosing facet joint–related pain and offering advanced non-surgical treatment options to help patients regain function and improve quality of life.
What Is Facet Joint Syndrome?
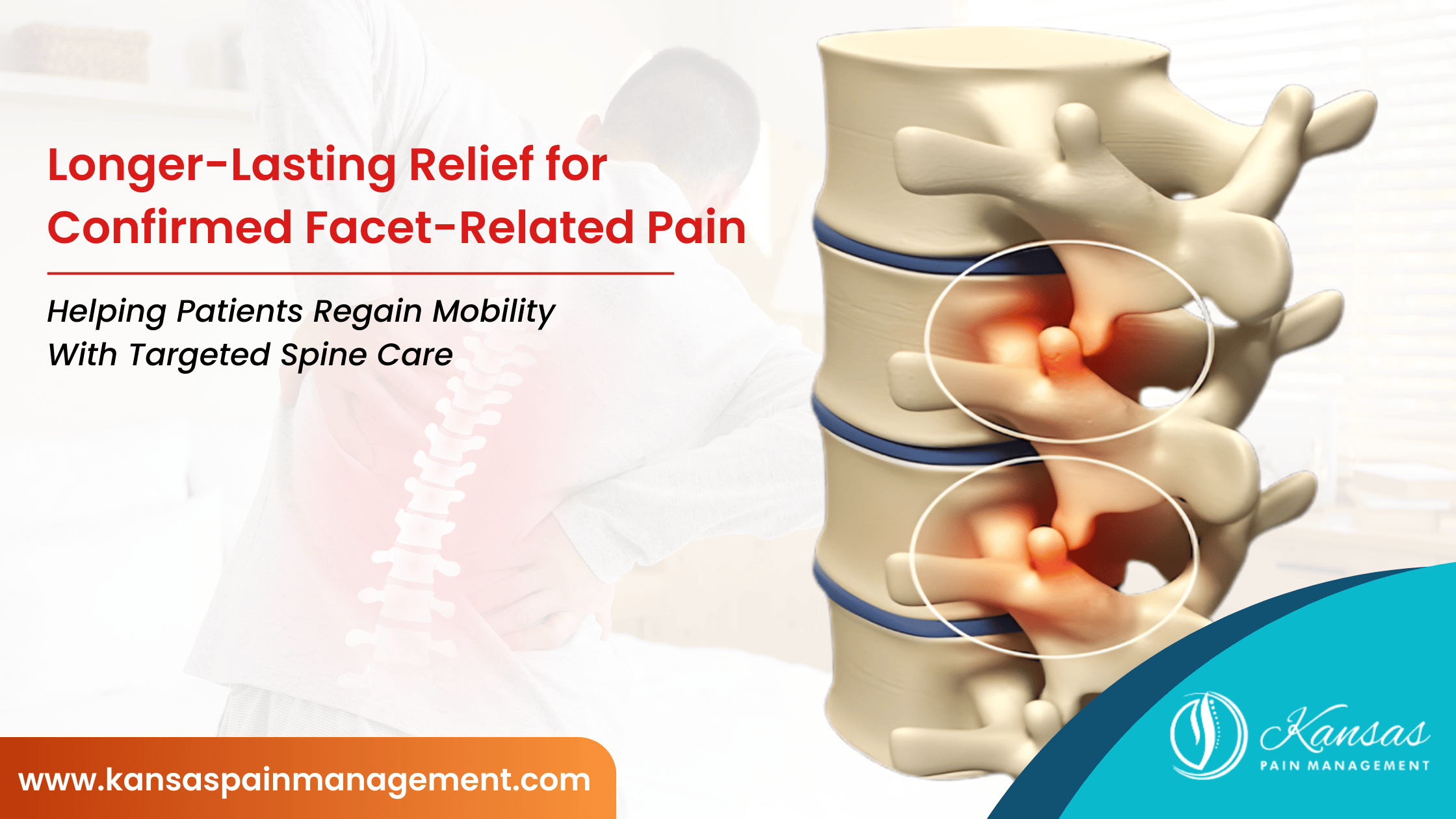
Facet Joint Syndrome occurs when one or more facet joints in the cervical (neck), thoracic (mid-back), or lumbar (lower back) spine become inflamed, arthritic, or injured. These joints guide spinal movement and provide stability. Over time, wear and tear or injury can cause degeneration, leading to pain during motion or prolonged positioning.
Common Symptoms of Facet Joint Syndrome
Symptoms vary based on the location of the affected joint but often include:
1. Localized Neck or Back Pain
- Dull, aching pain near the spine
- Pain that worsens with bending, twisting, or extending the spine
2. Referred Pain
- Neck pain that may radiate to the shoulders or upper back
- Lower back pain that may spread to the hips or buttocks
3. Stiffness and Reduced Range of Motion
- Morning stiffness or stiffness after inactivity
- Difficulty standing upright or turning the neck
4. Pain With Certain Movements
- Pain while arching the back
- Discomfort when transitioning from sitting to standing
Unlike disc-related pain, facet joint pain typically does not cause significant numbness or weakness in the arms or legs.
Causes of Facet Joint Syndrome
Facet joint pain can develop for several reasons, including:
- Degenerative arthritis due to aging
- Repetitive stress or overuse
- Poor posture or spinal misalignment
- Trauma or injury, such as whiplash or falls
- Obesity, which increases stress on spinal joints
Over time, cartilage breakdown within the joint can result in inflammation and pain.
How Is Facet Joint Syndrome Diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis is key to effective treatment. At Kansas Pain Management, evaluation may include:
- Detailed medical history and physical examination
- Review of imaging studies such as X-rays or MRI
- Diagnostic facet joint or medial branch nerve blocks to confirm the pain source
Identifying facet joint involvement helps tailor treatment and avoid unnecessary procedures.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Facet Joint Pain
Most patients with Facet Joint Syndrome respond well to conservative and minimally invasive care.
1. Medications
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Muscle relaxants or nerve-targeted medications when appropriate
2. Physical Therapy
Structured physical therapy can:
- Improve flexibility and spinal stability
- Reduce stiffness and muscle tension
- Promote proper posture and movement mechanics
3. Interventional Pain Management Procedures
For persistent pain, minimally invasive options may include:
- Facet joint injections
- Medial branch nerve blocks
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for longer-lasting relief
These procedures are designed to reduce inflammation and interrupt pain signals without surgery.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
- Weight management
- Ergonomic adjustments at work
- Low-impact exercise programs
Why Choose Kansas Pain Management?
At Kansas Pain Management, we focus on identifying the true source of spine-related pain and delivering individualized, non-surgical solutions. Our goal is to help patients reduce pain, restore movement, and avoid unnecessary surgery whenever possible.
When Should You See a Pain Specialist?
You should consider seeing a pain management specialist if:
- Neck or back pain lasts longer than a few weeks
- Pain worsens with movement or daily activities
- Conservative care has not provided lasting relief
Early evaluation can prevent chronic pain progression.
Schedule an Appointment
If you suspect Facet Joint Syndrome or are struggling with chronic neck or back pain, Kansas Pain Management is here to help. Contact us today to schedule a comprehensive evaluation and explore advanced non-surgical treatment options.